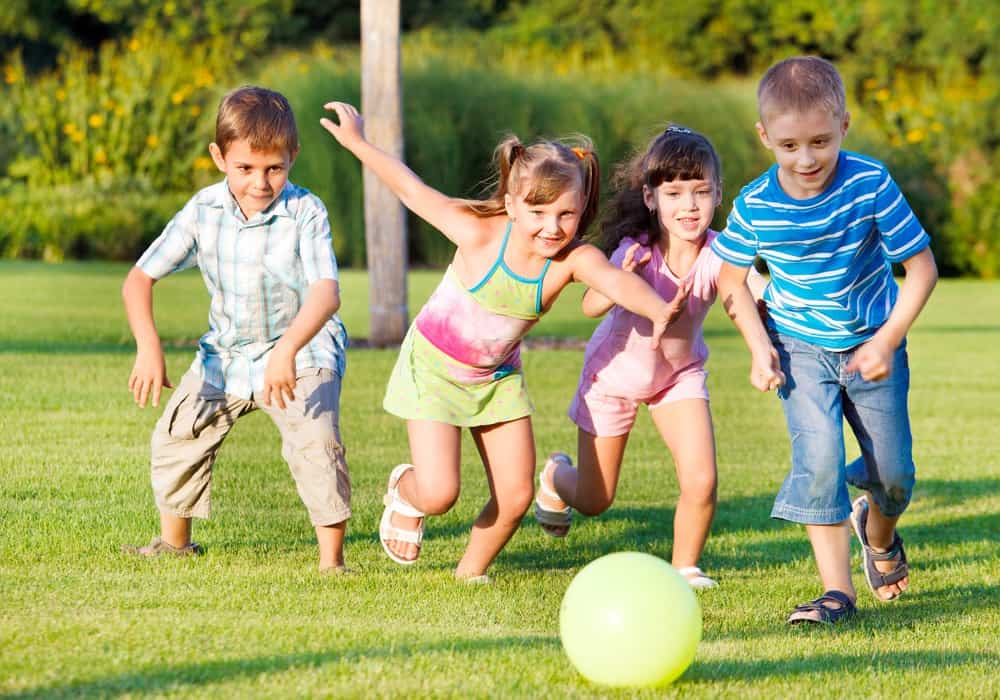

How To Tell the Difference Between ADHD and APD
Auditory processing disorder (APD) is thought to be a central nervous system dysfunction involving the way the brain processes auditory input. Children with APD primarily experience difficulty interpreting speech because they are unable to recognize important differences between word sounds. For example, a child with APD may confuse the meaning of the words “ball” with “wall” or “bat” with “cat”, especially when they are in environments with background noises, such as playgrounds, cafeterias and classrooms.
Symptoms of APD in children include:
- Being easily distracted, forgetful and disorganized
- Problems following directions in school and at home
- Acting upset or unsettled in noisy places
- Academic difficulties particularly involving subjects that require the child to hear and interpret a teacher’s instructions
Signs of auditory process disorder are often misdiagnosed as signs of ADHD because many symptoms of both conditions overlap. However, ADHD is not a central nervous system disorder but a neurodevelopmental and behavioral disorder that does not involve problems with the way the brain processes auditory information. Instead, children with ADHD are hyperactive, have poor impulse control and procrastinate when given a task to complete. ADHD is impairment of the brain’s “executive functioning” area found in the prefrontal lobe of the brain.
A child suspected of having APD or ADHD should be given the appropriate tests necessary to determine if they have one disorder or both disorders. Testing for APD includes hearing, language and speech assessments and cognitive testing which can show how well the child’s brain is processing information. Tests for ADHD include gathering first-hand information about the child’s behaviors from parents, teachers and school records and having a psychologist interview and observe the child.

What to Know About Noise-Induced Hearing Loss and How to Prevent It:
Hearing Loss
Beyond the Ringing: Tinnitus Treatment and Management Options at PAS
Common Questions - General
OTC vs. Prescription Hearing Aids: Why a Professional Evaluation is Your Best First Step
Hearing Aids



Share this entry